Read and Write CSV File using H2 Tools
Oct 2, 2015
1. Overview
H2 is a Java relational database. This is an open source database with a small footprint and supports JDBC. The database can be used with embedded, server or in-memory modes.
The H2 software can be downloaded and installed from http://www.h2database.com/. In the install directory:
- The
docsdirectory has the user manuals and the API javadocs. - The
bindirectory has theh2-1.3.176.jarfile. This jar file is required to be in classpath to compile and run the Java code using H2 database or tools. This jar file includes the JDBC driver software.
In addition to the standard database features, H2 has functions to read and write CSV (Comma Separated Value) files. There are two ways to use the CSV read and write functions:
- A CSV file can be read from or written to a H2 database table. This function uses the database engine. This function is provided by the H2 database API.
- A CSV file can be read from or written to from a Java application. This function does not use the H2 database engine. The API is from the H2 Tools and Java SE.
This article shows an example Java program to read and write CSV files using H2 Tools API. This does not use the database engine.
2. Reading a CSV file
A CSV file can be created using a text editor like Windows Notepad or a MS Excel program (save Excel sheet as a CSV file). Here is an example CSV file data:
FIRST, LAST, CITY, COUNTRY
fname1, lname1, city1, country1
fname2, lname2, city2, country2
fname3, lname3, city3, country3The data file has four rows. The first row is the header row; and this has the column headings (FIRST, LAST, CITY, COUNTRY). The next three rows are the data.
The example program reads the file and prints the header and data rows to the DOS console. The following steps with code snippets explain this.
2.1. Read the CSV File
ResultSet rs = new Csv().read(inFileName, null, null);The Csv class is part of H2 tools API and is used to read from and write to CSV files. ResultSet is the java.sql.ResultSet interface.
The read() method reads the file inFileName and creates a ResultSet object with the file contents. The method parameters:
- fileName - the input CSV file name
- colNames - column names or
nullif the column names should be read from the CSV file - charset - the character set or
nullto use the system default
2.2. Get the Column Names
The following code snippet prints the CSV file header column names to the console.
ResultSetMetaData meta = rs.getMetaData();
int noOfCols = meta.getColumnCount();
for (int i = 0; i < noOfCols; i++) {
System.out.print(meta.getColumnLabel(i + 1));
}2.3. Get the Row Data
The following code snippet prints each data row's column's to the console as a line. The three data rows are printed as three lines.
while (rs.next()) {
for (int i = 0; i < noOfCols; i++) {
System.out.print(rs.getString(i + 1));
}
}Note the Csv class's read() method and ResultSet interface methods throw java.sql.SQLException.
3. Writing to a CSV File
The SimpleResultSet class of H2 Tools API is used to write the CSV file. SimpleResultSet is a simple implementation of java.sql.ResultSet interface.
The data being written to the CSV file has the header row as well as the data rows. The following example shows how to create a file with two header columns (header row) and three data rows.
3.1. Create a SimpleResultSet
SimpleResultSet rs = new SimpleResultSet();3.2. Add Column Header Row
rs.addColumn("NAME", Types.VARCHAR, 255, 0);
rs.addColumn("COUNTRY", Types.VARCHAR, 255, 0);The above code snippet adds two column names (NAME and COUNTRY) to the header row.
3.3. Add Data Rows
Object [] rowData1 = new Object [] {"name1", "country1"};
Object [] rowData2 = new Object [] {"name2", "country2"};
Object [] rowData3 = new Object [] {"name3", "country3"};
rs.addRow(rowData1);
rs.addRow(rowData2);
rs.addRow(rowData3);The above code snippet creates three data rows and adds them to the result set. Note that the each data row is an Object array; and the each column data is the array element.
3.4. Write to CSV File
new Csv().write(fileName, rs, null);The write() method of the Csv class of H2 Tools API creates the CSV file fileName with the contents of the SimpleResultSet rs. The last parameter of the method specifies the character set; a String or a null in case of default system value.
Note the Csv class's write() method throws java.sql.SQLException.
3.5. Verify CSV File Contents
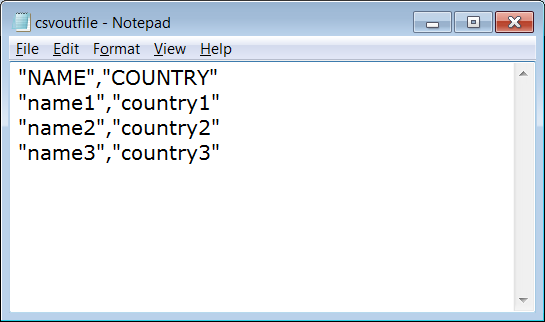
Open the CSV file using a Windows Notepad or MS Excel program and verify the contents. The file contents will look like this when opened with a Notepad:
4. Download
Download source code here: CsvH2ToolsExample.zip
NOTE: The example uses Java SE 7 and H2 version 1.3.176. The h2-1.3.176.jar file must be in the classpath to compile and run the code.
5. Useful Links and Notes
- Java SE 7 JDBC API: http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/sql/package-summary.html
- H2 Database API Javadocs: http://www.h2database.com/javadoc/index.html
There are various tools to read and write CSV files: Java SE API and tools from csvreader.com or Apache Commons CSV are some of them.
Return to top